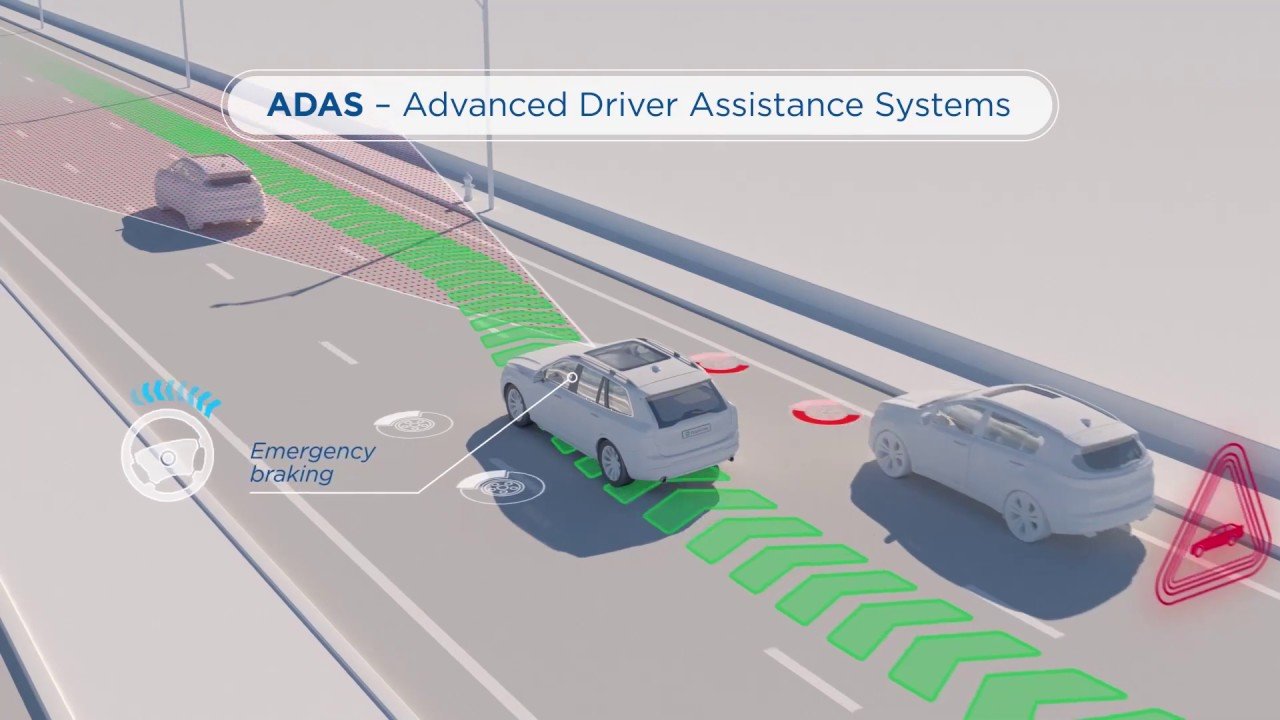
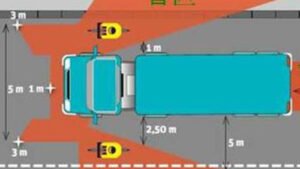
Introduction to Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS)
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) represent a pivotal evolution in the automotive industry, significantly transforming the landscape of vehicle safety and operational efficiency. These systems utilize an array of sensors, cameras, and artificial intelligence algorithms to aid drivers in various aspects of vehicle operation, thereby reducing the risk of accidents and enhancing overall transportation safety. With the growing complexities of long-distance freight and dangerous goods transportation, the integration of ADAS into commercial vehicles has become increasingly essential.
The primary purpose of ADAS is to mitigate human errors, which are a leading cause of vehicular accidents. By providing real-time feedback and alerts to the driver, these systems facilitate safer navigation on busy highways and during challenging driving conditions. Features such as lane departure warning, adaptive cruise control, and collision avoidance systems exemplify how ADAS technologies work collaboratively to support drivers in making informed decisions on the road.
An additional advantage of ADAS lies in its capability to monitor vehicle performance and operational metrics, enhancing the efficiency of long-distance transportation operations. For instance, in the context of freight transportation, ADAS can optimize route planning and enable more efficient fuel consumption. As a result, logistics companies can achieve significant cost savings while also reducing their carbon footprint, aligning with broader sustainability goals. Moreover, the implementation of these advanced systems in vehicles transporting dangerous goods contributes to enhanced safety measures, minimizing hazards associated with the transportation of such materials.
As the automotive landscape continues to evolve with the integration of technology, the future of transportation will undoubtedly see increased reliance on ADAS. These systems not only safeguard drivers and cargo but also represent an alignment with modern efficiency and safety standards. Understanding the mechanisms and benefits of ADAS is crucial for stakeholders in freight and hazardous materials transportation as they navigate this transformative phase.
Key Components of ADAS
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) incorporate a variety of technologies designed to improve vehicular safety and navigation, particularly in long-distance freight and dangerous goods transportation. Central to the functioning of ADAS are the key components: radar, cameras, and sensors. Each of these technologies plays a critical role in providing accurate, real-time data about the vehicle’s surroundings.
Radar systems are particularly pivotal in ADAS applications. They work by emitting radio waves that bounce off nearby objects, allowing the vehicle to detect distances and speeds of other vehicles or obstacles. This technology is fundamental for features like adaptive cruise control, which automatically adjusts the vehicle’s speed to maintain a safe following distance from the vehicle ahead.
Cameras are another essential component of ADAS. They provide visual data that can be used for various safety measures. For instance, lane-keeping assistance utilizes cameras to monitor lane markings on the road, helping drivers stay within their lanes. Moreover, rear-view cameras enhance the safety of reversing maneuvers by providing a clear view of the area behind the vehicle, minimizing the risk of collisions.
Sensors contribute to the effectiveness of ADAS by monitoring a multitude of variables, from weather conditions to road surface quality. They help in collision detection by utilizing sonar or ultrasonic waves to assess distances and identify potential hazards. Such technology ensures that timely warnings are issued to drivers, allowing them to take action and avoid accidents.
When all these components work in synergy, they significantly enhance the vehicle’s operational safety and efficiency. Together, radar, cameras, and sensors enable various advanced features that are helping to transform the future of transportation, especially in contexts involving long-distance and hazardous cargo transport.
Benefits of ADAS in Long-Distance Freight Operations
The integration of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) into long-distance freight operations presents numerous advantages that significantly enhance safety and operational efficiency. One of the most notable benefits is the increase in safety for both drivers and other road users. ADAS technologies such as collision avoidance systems, lane departure warnings, and adaptive cruise control are designed to mitigate the risks associated with long-haul driving. The implementation of these systems has been shown to reduce accident rates, leading to safer transportation of goods over extended distances.
In addition to increased safety, ADAS substantially contributes to the reduction of driver fatigue. Long-haul trucking can be arduous, often requiring drivers to remain alert for extended periods. Features such as automatic emergency braking and lane-keeping assist can relieve some of the burdens on drivers, allowing them to focus on monitoring road conditions rather than constantly managing the vehicle. This support can lead to better decision-making and a decrease in the likelihood of accidents caused by fatigue.
Moreover, the efficiency of fuel consumption can be markedly improved through the use of ADAS technologies. Many systems help optimize speed and driving patterns, which can lead to reductions in fuel wastage during long trips. According to recent statistics, fleets that have adopted ADAS have reported an average fuel efficiency improvement of up to 10%. This not only results in significant cost savings for companies involved in freight transportation but also contributes to the reduction of carbon emissions, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Case studies from various freight operators demonstrate the positive impact of ADAS on performance metrics. Operators who integrated ADAS reported improved delivery times and reduced operational costs. The advanced analytics provided by these systems further enable companies to enhance route planning and vehicle maintenance schedules. Overall, the benefits of ADAS integration into long-distance freight operations are varied and impactful, presenting a path towards a more efficient, safe, and sustainable future in the transportation of goods.
Challenges and Limitations of ADAS
As Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) continue to evolve, their implementation in long-distance freight and dangerous goods transportation faces several challenges and limitations. Technological barriers are among the foremost hurdles. The integration of sophisticated sensors, cameras, and software necessary for ADAS prevalence requires substantial investments in infrastructure and ongoing maintenance. Many existing vehicles may not be equipped with the necessary technology, necessitating significant retrofitting or outright replacement of older fleets to incorporate these advanced safety features.
Regulatory concerns also play a pivotal role in the broader adoption of ADAS in the transportation industry. Legislation surrounding the use of these systems varies by region, presenting inconsistencies that complicate compliance. An environment characterized by disparate regulations may deter companies from investing in ADAS. Additionally, the lack of comprehensive guidelines can create ambiguity around liability in the event of an accident involving ADAS-equipped vehicles, raising concerns for stakeholders in the freight and transportation sectors.
Driver training is another crucial aspect when considering the limitations of ADAS. While these systems are designed to assist drivers, they do not replace the need for skilled operators behind the wheel. An over-reliance on these technologies may detract from driver vigilance and the ability to assess complex road conditions. Continuous engagement and situational awareness are essential, as drivers must remain prepared to take control of the vehicle in emergency situations. Hence, adequate training programs are crucial to strike a balance between technological dependency and driver competency.
In light of these challenges, industry stakeholders must address the technological, regulatory, and operational dimensions of ADAS to harness its full potential while ensuring safety and efficiency in long-distance freight and dangerous goods transportation.
ADAS for the Transportation of Dangerous Goods
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) play a crucial role in enhancing safety and compliance in the transportation of dangerous goods. The sector involves specific challenges due to the inherent risks associated with hazardous materials, demanding specialized strategies to mitigate potential threats. By employing advanced technologies, such as adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assistance, and emergency braking systems, ADAS significantly contributes to safer transport logistics.
One primary application of ADAS in this niche is the integration of collision avoidance systems that utilize sensors and cameras to detect potential hazards on the road. For example, vehicles transporting flammable materials can benefit from these systems by receiving alerts about obstacles or rapidly changing traffic conditions. Efficient use of such technology ensures that drivers can react promptly, reducing the likelihood of accidents that could lead to catastrophic spills or explosions.
Moreover, compliance with strict regulatory requirements is paramount in the transportation of dangerous goods. ADAS assists in maintaining adherence to these regulations through features that monitor compliance with speed limits and route management, particularly in sensitive areas. For instance, geofencing capabilities can restrict vehicles from entering zones where hazardous materials may pose additional risks, thereby allowing companies to adhere to local regulations more readily.
Real-world implementations showcase the efficacy of ADAS in this sector. Companies such as Schneider National have successfully utilized collision warning systems to improve safety while transporting chemicals and other hazardous materials. Similarly, some logistics firms have reported lower incident rates and improved delivery times as a direct result of integrating ADAS technology into their freight operations. These instances provide a compelling case for the broader adoption of such systems in dangerous goods transportation, promising a safer and more efficient future.
Future Trends in ADAS Technology
The landscape of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) is undergoing rapid transformation, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and sensor fusion. As the transportation sector evolves, particularly in long-distance freight and dangerous goods transportation, these technologies hold the promise of significantly enhancing safety and operational efficiency.
One of the most notable trends is the integration of artificial intelligence into ADAS. With AI algorithms capable of analyzing vast amounts of data in real time, vehicles can make faster, more informed decisions. This capability is particularly crucial in the context of long-haul freight transportation, where the reliability and safety of deliveries are paramount. AI can predict potential hazards, adapt to changing road conditions, and optimize route planning, ensuring minimal disruptions and reduced delivery times.
Machine learning is another key component, enabling systems to improve over time through experience. By continuously analyzing driving patterns and environmental data, machine learning enhances the system’s ability to recognize various scenarios and respond appropriately. As a result, the implementation of machine learning into ADAS can lead to a marked decrease in accident rates and an increase in the overall efficiency of logistics operations.
Additionally, innovations in sensor fusion are set to further revolutionize ADAS technology. By combining data from multiple sensors, such as cameras, radar, and lidar, these systems can generate a comprehensive understanding of a vehicle’s surroundings. This holistic view enhances situational awareness, leading to more effective responses to potential threats on the road. In long-distance freight scenarios, the improved perception of the driving environment will help in navigating complex traffic situations, particularly when transporting dangerous goods.
As the future of transportation continues its rapid evolution, the incorporation of AI, machine learning, and sensor fusion will undoubtedly define advanced driver assistance systems. The convergence of these technologies will not only improve safety in long-distance freight transport but also streamline operations, paving the way for a more efficient logistics industry.
The Role of Regulatory Bodies in ADAS Implementation
The implementation of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) in long-distance freight and dangerous goods transportation heavily relies on the involvement of regulatory bodies. These organizations are integral to establishing a framework that ensures the safety and effectiveness of these sophisticated technologies. By developing and enforcing regulations, regulatory bodies help create standards that manufacturers must adhere to when designing and deploying ADAS solutions in commercial vehicles.
Primarily, regulations set forth guidelines for the technical specifications of ADAS technologies. This includes standards regarding functionalities such as collision avoidance, lane departure warnings, and adaptive cruise control. Regulatory bodies also monitor the performance and reliability of these systems through rigorous testing protocols before they are approved for commercial use. Such measures not only ensure that the technology operates as intended but also contribute to the overall safety of transport operations involving hazardous materials.
Furthermore, collaboration between manufacturers, operators, and policymakers is crucial during the integration of ADAS. Regulatory bodies often act as facilitators in discussions among these stakeholders, ensuring that the diverse needs and concerns of all parties are addressed. This collaboration is essential for creating regulations that reflect real-world complexities and promote safe transportation practices. Additionally, ongoing dialogue can lead to the adaptation of regulations as technology evolves and new challenges arise in the freight and dangerous goods sectors.
As ADAS technology continues to advance, regulatory bodies will play an essential role in shaping its future. They must remain vigilant in updating regulations to keep pace with innovations while ensuring that public safety and environmental concerns are not compromised. The proactive involvement of these organizations is vital for the successful integration of ADAS into the transportation infrastructure, thereby enhancing efficiency and safety in moving freight and dangerous goods.
Case Studies: Successful ADAS Implementations
The implementation of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) has been transformative for various companies within the long-distance freight and dangerous goods transportation sectors. Several notable case studies exemplify the successful integration of these technologies, highlighting both challenges faced and benefits realized.
One prominent example is XYZ Logistics, a major player in the freight industry. The company incorporated lane departure warning systems and adaptive cruise control into its fleet. Initially, the transition faced resistance from drivers who were accustomed to traditional driving methods. Training sessions focusing on the benefits of ADAS technologies, such as increased safety and reduced accident rates, helped to alleviate concerns. Following the implementation, XYZ Logistics reported a significant reduction in collision incidents, which translated into lower insurance premiums and enhanced road safety records.
Another interesting case is ABC Transport, which specializes in the transportation of hazardous materials. This company opted to implement emergency braking systems and blind-spot detection features in response to increasing regulatory pressures and safety requirements. The challenge they encountered was the integration of these technologies with their existing fleet management systems. Through collaboration with technology providers and extensive pilot testing, ABC Transport managed to create a seamless integration. As a result, they experienced a marked improvement in driver awareness and reaction times in critical situations, resulting in a decline in near-miss accidents.
Furthermore, DEF Carriers is a third case showcasing the potential of ADAS. They introduced collision avoidance systems across their long-haul fleet, driven by an objective to enhance safety while maintaining delivery schedules. Although the implementation phase required significant investments and adjustments to business operations, the long-term benefits have been substantial. DEF Carriers reported decreased downtime due to accidents, increased vehicle longevity, and higher customer satisfaction due to timely deliveries.
These case studies illustrate the practical applications of ADAS technologies within the transportation sector, underscoring their potential to improve safety and operational efficiency. As more companies navigate the challenges of implementation, these examples serve as useful references for understanding the transformative power of ADAS in freight and dangerous goods transportation.
Conclusion: The Impact of ADAS on the Future of Transportation
As the transportation industry moves towards embracing advanced technologies, Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) are proving to be transformative. The integration of ADAS into long-distance freight and the transportation of dangerous goods serves to enhance safety, efficiency, and regulatory compliance within this critical sector. These innovative systems—ranging from collision avoidance technologies to automated lane keeping—are designed to significantly reduce human error, which is a leading cause of accidents in freight transport. The implementation of these systems ensures that operators are better equipped to manage their vehicles, thereby minimizing the risks associated with long hauls and hazardous materials transport.
Moreover, the efficiency gains achieved through ADAS cannot be overstated. By optimizing driving patterns and enhancing route planning, these technologies help ensure timely deliveries while also conserving fuel, thereby contributing to cost reduction. In an era where logistics efficiency directly affects customer satisfaction and business profitability, ADAS can play a pivotal role in redefining operational standards. Freight companies adopting these systems can expect not only to streamline their operations but also to cultivate a reputation as safety-conscious and forward-thinking entities.
In terms of compliance, ADAS fulfills regulatory requirements by providing a framework for enhanced monitoring and reporting of driving behavior. This is particularly crucial in the context of transporting dangerous goods, where stricter regulations are in place. With these systems, companies can ensure better adherence to safety protocols and demonstrate accountability through accurate records of vehicle performance and driver actions.
Ultimately, viewing Advanced Driver Assistance Systems as an essential investment for the future of transportation is imperative. Not only do they address the pressing challenges of safety, efficiency, and compliance, they also represent a commitment to technological advancement that will shape the logistics landscape for years to come.