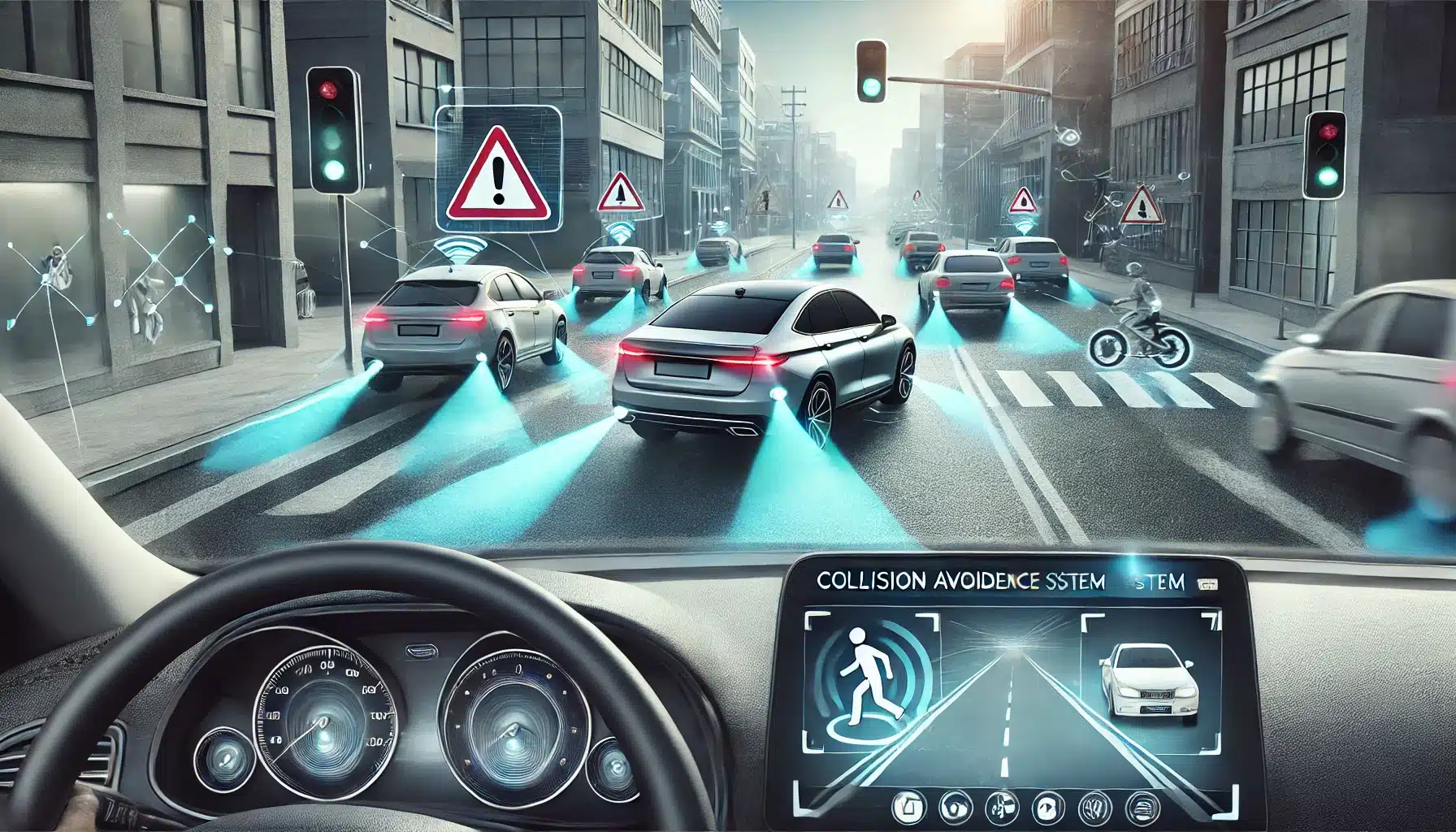
Collision avoidance systems (CAS) are at the forefront of automotive safety technology, designed to prevent accidents by detecting potential collisions and taking proactive measures. These systems, which utilize advanced sensors, cameras, and AI, are revolutionizing how vehicles navigate roads, enhancing driver safety, and paving the way for autonomous driving. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the technology, benefits, applications, and future trends of collision avoidance systems.
What Are Collision Avoidance Systems?
Collision avoidance systems are technologies integrated into vehicles to detect potential accidents and either warn the driver or take corrective actions to avoid collisions. According to NHTSA, these systems use a combination of radar, cameras, ultrasonic sensors, and AI algorithms to monitor the vehicle’s surroundings and identify hazards.
How Collision Avoidance Systems Work
The functionality of CAS is based on real-time data collection and processing. Here’s how it typically operates:
- Detection: Sensors and cameras continuously monitor the vehicle’s surroundings, including other vehicles, pedestrians, and obstacles.
- Assessment: The system evaluates the collected data to determine the likelihood of a collision based on the vehicle’s speed, trajectory, and distance from obstacles.
- Alert: If a potential collision is detected, the system issues visual, auditory, or tactile warnings to alert the driver.
- Intervention: Advanced systems can automatically apply brakes, adjust steering, or reduce acceleration to prevent a collision.
Key Components of Collision Avoidance Systems
Modern CAS consists of several critical components that work together seamlessly:
- Radar Sensors: Measure the distance and speed of objects in the vehicle’s path.
- Cameras: Provide visual data for detecting road markings, pedestrians, and obstacles.
- Ultrasonic Sensors: Monitor nearby objects for low-speed maneuvers like parking.
- Control Units: Process sensor data and decide on corrective actions.
- Actuators: Execute automatic interventions like braking or steering adjustments.
Types of Collision Avoidance Systems
CAS can be categorized based on their functionality:
1. Forward Collision Warning (FCW)
FCW systems monitor the area in front of the vehicle and warn the driver of potential collisions with other vehicles or obstacles.
2. Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB)
AEB systems automatically apply the brakes when a collision is imminent and the driver fails to react in time.
3. Lane Departure Warning (LDW) and Lane Keeping Assist (LKA)
LDW systems alert drivers when they unintentionally drift out of their lane, while LKA actively steers the vehicle back into its lane.
4. Blind Spot Detection
These systems monitor blind spots and warn drivers of vehicles or objects in adjacent lanes.
5. Rear Cross-Traffic Alert (RCTA)
RCTA warns drivers of approaching traffic when reversing out of parking spaces or driveways.
Benefits of Collision Avoidance Systems
1. Enhanced Safety
CAS significantly reduces the likelihood of accidents by providing timely warnings and interventions. According to the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS), vehicles equipped with AEB experience 50% fewer rear-end collisions.
2. Reduced Driver Fatigue
By assisting with tasks like lane keeping and adaptive cruise control, CAS minimizes the cognitive load on drivers, reducing fatigue during long journeys.
3. Lower Insurance Costs
Many insurers offer discounts for vehicles equipped with advanced safety systems, as they lower the risk of accidents and claims.
4. Support for Autonomous Driving
CAS technologies are foundational for the development of fully autonomous vehicles, enabling them to navigate complex traffic scenarios safely.
Applications of Collision Avoidance Systems
1. Passenger Vehicles
CAS is widely adopted in passenger cars to enhance driver safety and convenience. Features like adaptive cruise control and lane-keeping assist are common in modern vehicles.
2. Commercial Vehicles
For commercial fleets, CAS helps prevent costly accidents and ensures compliance with safety regulations. Companies like Samsara offer fleet management solutions that integrate CAS technologies.
3. Public Transport
CAS is used in buses and trains to avoid collisions with other vehicles and pedestrians, ensuring passenger safety.
4. Industrial Equipment
In industries like construction and mining, CAS prevents accidents involving heavy machinery, safeguarding workers and equipment.
Future Trends in Collision Avoidance Systems
The evolution of CAS is driven by advancements in technology and the push towards autonomous driving. Key trends include:
1. Integration with AI
AI enhances the decision-making capabilities of CAS, enabling systems to predict and respond to complex traffic scenarios more effectively.
2. V2X Communication
Vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication allows CAS to exchange data with other vehicles and infrastructure, improving situational awareness.
3. Improved Sensor Fusion
Combining data from multiple sensors enhances the accuracy and reliability of CAS, reducing false positives and negatives.
4. Wider Adoption in Budget Vehicles
As production costs decrease, CAS features are becoming accessible in mid-range and budget vehicles, democratizing safety.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its benefits, CAS faces several challenges:
- High Costs: Advanced CAS features can significantly increase vehicle costs.
- Technical Limitations: Current systems may struggle in adverse weather conditions or complex traffic scenarios.
- Driver Overreliance: Overreliance on CAS can lead to complacency and reduced attentiveness.
Conclusion
Collision avoidance systems are transforming road safety by preventing accidents and saving lives. With continuous advancements in technology, these systems are becoming more effective and accessible, paving the way for a future of autonomous driving. Whether in passenger cars, commercial fleets, or industrial equipment, CAS is an invaluable asset that enhances safety, efficiency, and confidence on the road. Explore the latest developments in CAS to experience the benefits of this revolutionary technology.