Introduction to Driver Monitoring Systems (DMS)
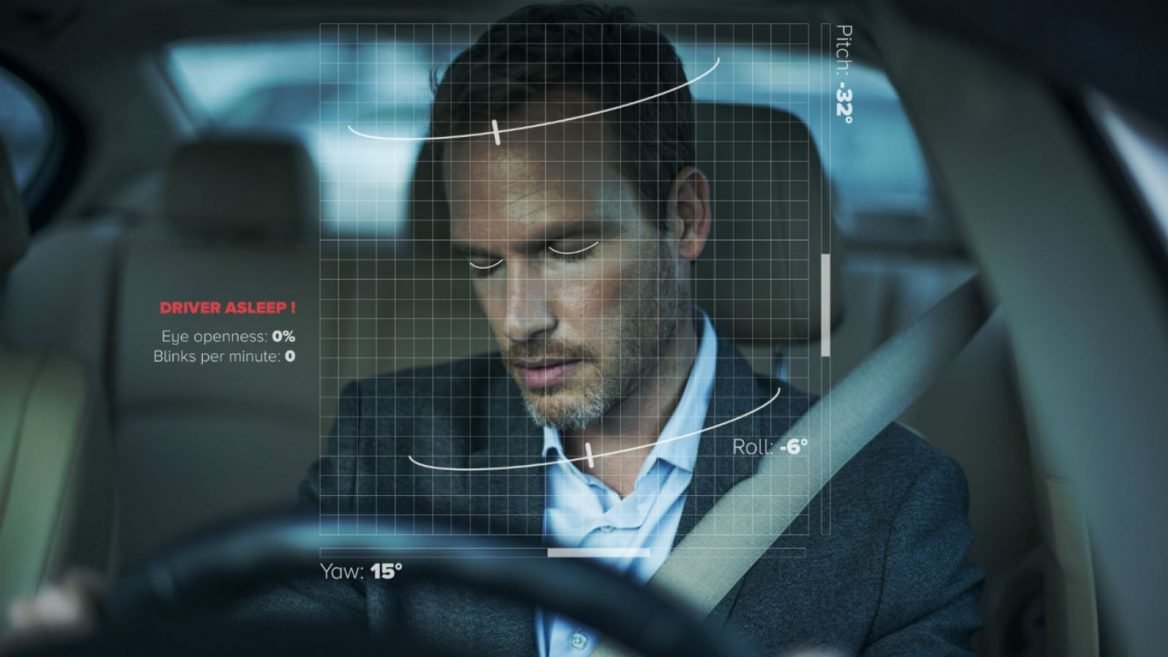
A Driver Monitoring System (DMS) represents a critical advancement in automotive safety technology, designed to enhance both driver performance and road safety. The primary purpose of a DMS is to continuously monitor the behavior and alertness of the individual behind the wheel. This system utilizes an array of sensors, typically integrated within the vehicle’s interior, that are responsible for assessing various indicators of driver engagement and attentiveness.
Central to the functionality of DMS are technologies such as cameras, infrared sensors, and machine learning algorithms. These components work in concert to track key metrics, including eye movements, head position, and even facial expressions, providing real-time data on the driver’s state. By analyzing these indicators, the system can identify signs of drowsiness, distraction, or lack of focus, thereby alerting the driver to potential hazards before they become critical. For instance, if the system detects that the driver’s eyes are closing or are not fixated on the road, it may issue visual or auditory warnings to re-engage the driver.
The significance of DMS lies not only in its ability to safeguard drivers but also in its potential to mitigate the risks associated with distracted driving. With distractions on the rise, integrating a DMS into vehicles serves as a proactive measure to address this pressing issue. By ensuring heightened awareness and responsiveness, DMS can play a pivotal role in preventing accidents that stem from driver inattention, establishing itself as an indispensable feature in modern vehicles. As automotive technology continues to evolve, Driver Monitoring Systems stand at the forefront of enhancing road safety and ensuring a more secure driving experience for everyone on the road.
Components of DMS and How They Work
Driver Monitoring Systems (DMS) comprise several key components that work in harmony to enhance road safety and driver performance. The primary elements include cameras, infrared sensors, and advanced software algorithms. Each of these components plays a crucial role in detecting driver behaviors such as drowsiness and distraction, allowing for timely interventions.
Cameras are fundamental to DMS. They are typically mounted on the vehicle’s dashboard or steering column and capture real-time images of the driver’s face. By continuously monitoring facial expressions, eye movements, and head position, cameras help identify signs of fatigue or inattention. High-definition cameras equipped with wide-angle capabilities ensure comprehensive coverage, which is vital for accurate detection.
Infrared sensors complement the visual data provided by cameras. These sensors are particularly useful in low-light conditions, allowing the DMS to operate effectively at night. They emit infrared light and measure the light reflected back from the driver’s face. By assessing eye closure duration and pupil dilation, infrared sensors can further ascertain the driver’s alertness state, providing critical input to the system.
Software algorithms are the brains of the DMS, processing the data collected from cameras and sensors. These algorithms are designed to analyze behavioral patterns and compare them against predefined thresholds for safe driving. For instance, if the system detects a significant deviation from normalized driving behavior, such as prolonged eye closure indicating drowsiness, it triggers alerts to warn the driver and prompts corrective measures.
Moreover, the integration of DMS with vehicle systems enables real-time feedback to the driver. When unsafe behavior is detected, the DMS may initiate various actions, such as audible alerts, visual warnings, or even activating autonomous vehicle systems to mitigate risks. This adaptive approach not only addresses immediate concerns but also fosters a culture of safety that can lead to improved driving habits over time.
Benefits of Implementing Driver Monitoring Systems
The adoption of Driver Monitoring Systems (DMS) has emerged as a significant advancement in ensuring road safety and enhancing driver performance across various types of vehicles, including personal cars, commercial fleets, and public transportation. One of the primary advantages of DMS is its ability to significantly reduce the incidence of accidents. By using advanced technologies such as eye-tracking and behavioral analysis, these systems can effectively identify signs of driver fatigue or distraction, allowing timely interventions that may prevent potential collisions. This proactive approach not only saves lives but also mitigates damage to vehicles and property.
Moreover, DMS contributes to improving driver performance directly. Through continuous monitoring, drivers receive real-time feedback regarding their behaviors, encouraging responsible driving practices. This not only fosters safer driving habits but also boosts overall confidence for both novice and experienced drivers. Enhanced driver performance leads to smoother riding experiences, reduced wear and tear on vehicles, and improved fuel efficiency as safe driving habits are correlated with optimized driving behavior.
In addition to safety and performance improvements, implementing DMS can yield considerable economic advantages, particularly for commercial fleet operators. Companies can benefit from lower accident rates, which directly translates into reduced insurance premiums. Moreover, the decrease in vehicle maintenance costs, as a result of safer driving patterns, further contributes to operational savings. Public transportation systems that embrace DMS may also experience increased patron trust and satisfaction, thereby encouraging higher ridership rates. Ultimately, the integration of Driver Monitoring Systems in modern vehicles presents a compelling value proposition, highlighting safety, performance enhancement, and cost-effectiveness as key benefits for all vehicle types.
Future Trends in Driver Monitoring Systems
As technology continues to evolve, Driver Monitoring Systems (DMS) are expected to undergo significant advancements, primarily driven by the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies. These innovations are enabling DMS to become more sophisticated in their ability to assess driver behavior and alertness. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, identifying patterns that indicate fatigue or distraction far more efficiently than traditional systems, which often rely on basic metrics.
Another area poised for growth is sensor technology. Future DMS will likely incorporate more advanced sensors capable of capturing a wider range of physiological indicators. For instance, innovations in biometric sensors could allow systems to monitor heart rate variability and pupil dilation, providing a comprehensive view of driver state. These advancements would enhance overall safety and improve vehicle interaction, ultimately contributing to a more responsive driving experience.
Data analytics will play a critical role in shaping the future of DMS. As systems gather and analyze data on driver behavior over time, they can provide personalized feedback and coaching to drivers. This not only promotes safer driving habits but also fosters a deeper understanding of individual preferences and requirements. Moreover, integrating DMS with other vehicle safety systems can facilitate a more interconnected automotive environment, where systems share information to make real-time adjustments and improve overall safety outcomes.
Furthermore, as the automotive industry adapts to stricter regulatory frameworks, the significance of DMS will increase. Future regulations may mandate the use of advanced driver monitoring technologies across various vehicle categories, thereby influencing consumer expectations. As stakeholders recognize the critical role of DMS in reducing accidents and enhancing road safety, manufacturers will likely focus on refining these systems, ensuring they meet and exceed emerging standards.